Greek mythology and astronomy are closely connected

Greece has been one of my dream destinations since I was a kid. Not because of their dreamy beaches, not the food, but because of the Greek mythology. As a lover of astronomy, it was inevitable for me to read all about Greek mythology that most of the Northern Hemisphere’s constellations are named after. I told the stories to the visitors while I was working at an astronomy observatory. Most of the constellations don’t really look like what they are supposed to, but some are, like Orion or Hercules. Greek Mythology is so broad, it would take a lifetime to understand the meaning and remember all the Gods and others. Here I named some of the most important gods and stories in Greek Mythology. If this doesn’t motivate you to travel to Greece, I don’t know what will!
Zeus, the center of Greek mythology
The king of gods, Zeus is the center of Greek Mythology. The youngest child of Cronus and Rhea, Zeus is married to Hera and fathered Ares, Hebe, and Hephaestus, but also has many partners and children with them. He is known for his erotic escapades. That led to many heroic offspring including Athena, Apollo, Hermes, Perseus, Heracles, and much more.

One of the most popular sites in Athens, The Temple of Zeus is located in Olympia. Only the ruins remain today. The column that has fallen and can still be seen on pieces was brought down during a thunderstorm about a century ago. The 1896 Olympic Stadium and Hadrian’s Arch are located nearby.
Hera
Hera is a complex woman. She is the wife and one of the three sisters of Zeus. She was the goddess of women and marriage. She was also the emblem of fertility. Jealousy and vengeance were often mentioned in her mythology. Juno is her name in Roman mythology.
The Greek name for the Milky Way (galaxies) is derived from the word milk (gala). One legend explains that the Milky Way was created by Heracles when he was a baby. He was a son of Zeus with a mortal woman Alcmene. Zeus let the infant Hercules suckle on his wife Hera’s milk when she was asleep, an act that would give the baby godlike qualities. When Hera woke up and realized, she pushed him away and the spurting milk became the Milky Way.

In a clear sky, you can observe the hazy band of white light across the sky. The center of the Milky Way lies in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius, which is the brightest.
The Temple of Hera is an ancient Doric Greek temple at Olympia. It was erected in 590 BC, and destroyed by an earthquake in the early 4th century and never rebuilt.
Andromeda
One of the autumn constellations in the northern sky, Andromeda contains a rather sad story. Andromeda is a daughter of Cepheus and Cassiopeia. Cassiopeia was jealous of Andromeda’s beauty. Cassiopeia ordered Andromeda to strip and chain naked to a rock as a sacrifice to state the monster, but she was saved from Perseus. Greek hero’s rescue of a beautiful woman is an important part of the mythology.
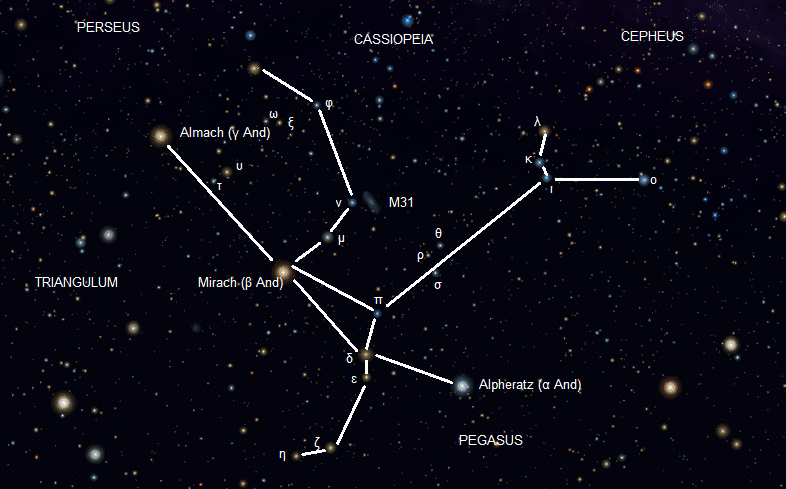
Her father Cepheus, mother Cassiopeia, and her rescuer Perseus can be found near Andromeda in the Northern Hemisphere in autumn. Cassiopeia is a guiding constellation to the North. Andromeda constellation also contains the neighboring galaxy, Andromeda (M31).
Hercules
The constellation Hercules is the fifth largest of the modern constellations that can be seen in the Summer sky in the Northern Hemisphere. It’s one of the constellations that actually look like what it’s supposed to. Hercules doesn’t contain any bright stars, but it can be easily found next to the Summer Triangle.
Hercules was the son of Zeus with a mortal woman Alcmene. Hercules is the Roman mythological hero adapted from the Green hero Heracles. Hercules is famous for his strength. He was the greatest of the Greek heroes, a paragon of masculinity. His iconographic attributes are the lion skin and the club.
Orion
One of the most recognizable constellations in the night sky, Orion was named after the great hunger in Greek mythology. Its brightest Alpha (Betelgeuse), Beta (Rigel), and the three stars of Orion’s Belt are easily recognizable.
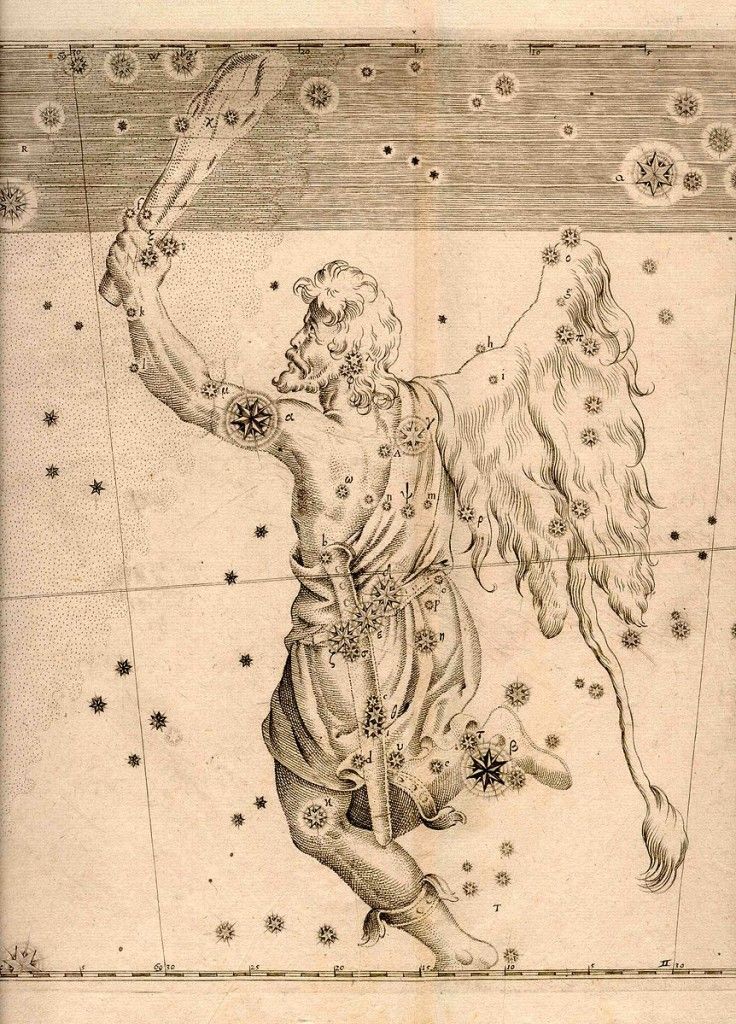
In Greek literature, he first appears as a great hunter in Homer’s Odyssey. Odysseus sees him hunting in the underworld with a bronze club, a great slayer of animals. In Iliad, Orion is described as a constellation, and Sirius is mentioned as his dog.
Orion, Canis Major, and Canis Minor can be seen in the winter sky in the Northern Hemisphere. The brightest star in the Northern Hemisphere, Sirius, is the alpha star of Canis Major.
Further reading about Greek mythology and astronomy
I love reading about mythologies. Not just Greek ones but from all cultures, including Nordic stories. One of my favorite story series of all time, the Lord of the Rings is also based on many different mythologies and hero legends. If you want to get into Greek mythology, I recommend Mythos by Stephen Fry. There are a lot of books out there but of course, Stephen Fry makes it more enjoyable. His audiobooks are also great!